The Quest for Safe Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Non-Chemical Sunscreens
Related Articles: The Quest for Safe Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Non-Chemical Sunscreens
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Quest for Safe Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Non-Chemical Sunscreens. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Quest for Safe Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Non-Chemical Sunscreens

The sun’s rays, while essential for life, can also be harmful, causing skin damage, premature aging, and even skin cancer. Sunscreen is a crucial tool for protecting our skin from these damaging effects. While many sunscreens rely on chemical filters to absorb ultraviolet (UV) radiation, a growing segment of consumers seeks alternatives that avoid potentially irritating or harmful chemicals. This guide explores the world of non-chemical sunscreens, providing a comprehensive understanding of their benefits, considerations, and how to choose the best option for your needs.
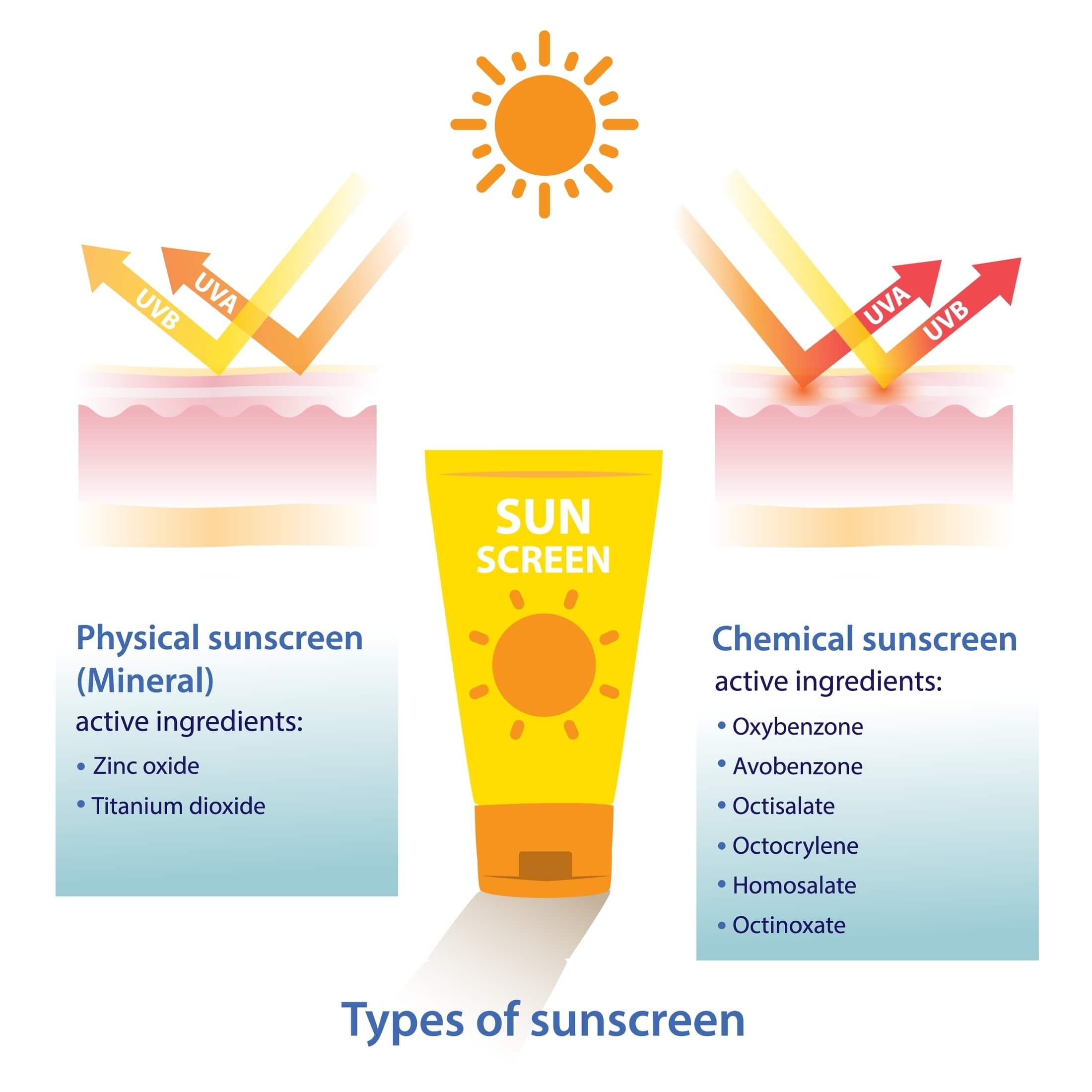
Understanding the Science: Chemical vs. Non-Chemical Sunscreens
Sunscreens fall into two primary categories: chemical and mineral.
-
Chemical Sunscreens: These sunscreens use organic compounds that absorb UV radiation and convert it into heat. Common chemical filters include oxybenzone, octinoxate, avobenzone, and octisalate. While effective at blocking UV rays, concerns exist about potential skin irritation, hormone disruption, and environmental impact.
-
Non-Chemical (Mineral) Sunscreens: These sunscreens utilize mineral ingredients, primarily zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, to create a physical barrier that reflects and scatters UV rays. They are considered safer for the skin and environment.
The Advantages of Non-Chemical Sunscreens:
-
Gentle on Sensitive Skin: Mineral sunscreens are generally gentler on sensitive skin and less likely to cause irritation, redness, or breakouts. They are often suitable for individuals with eczema, rosacea, or other skin conditions.
-
Environmentally Friendly: Mineral sunscreens are considered more environmentally friendly as they are less likely to harm marine life and coral reefs. Chemical filters can be harmful to aquatic ecosystems.
-
Broad-Spectrum Protection: Mineral sunscreens provide broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays, offering comprehensive protection against the full range of sun’s harmful radiation.
-
Stability and Durability: Mineral sunscreens are stable and do not break down easily in sunlight, ensuring long-lasting protection. They are also more resistant to water and sweat, making them ideal for outdoor activities.
-
Safe for Babies and Children: Mineral sunscreens are generally considered safe for babies and children, as they are less likely to be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Navigating the Options: Choosing the Right Non-Chemical Sunscreen
While mineral sunscreens offer numerous benefits, choosing the right product for your skin type and needs requires careful consideration.
-
Zinc Oxide vs. Titanium Dioxide: Both zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are effective mineral filters. Zinc oxide tends to be thicker and leave a white cast, while titanium dioxide is generally more transparent. The choice depends on individual preferences and skin type.
-
Formulation: Mineral sunscreens are available in various formulations, including lotions, creams, sticks, and sprays. Consider your skin type and personal preference when selecting a formulation.
-
SPF: The SPF (Sun Protection Factor) indicates the sunscreen’s ability to block UVB rays, which cause sunburn. Choose an SPF of 30 or higher for optimal protection.
-
Water Resistance: Look for water-resistant sunscreens if you plan to be in the water or sweating heavily.
-
Ingredients: Pay attention to the full ingredient list and avoid products containing potentially irritating or harmful additives.
-
Fragrance and Additives: Some mineral sunscreens contain fragrances and other additives that can irritate sensitive skin. Opt for fragrance-free and hypoallergenic options for sensitive skin.
Beyond the Basics: Addressing Common Concerns
-
White Cast: While mineral sunscreens can leave a white cast, advancements in technology have produced formulations that are more transparent. Look for products labeled as "non-nano" or "micro-sized" for better blending.
-
Texture and Feel: Some mineral sunscreens can feel thick or heavy on the skin. Consider formulations specifically designed for facial use, which are often lighter and more easily absorbed.
-
Cost: Mineral sunscreens can be slightly more expensive than chemical sunscreens. However, their safety and environmental benefits justify the investment in long-term skin health.
FAQs about Non-Chemical Sunscreens:
- Q: Are mineral sunscreens effective?
A: Yes, mineral sunscreens are highly effective in protecting the skin from UV radiation. They create a physical barrier that reflects and scatters UV rays, providing broad-spectrum protection.
- Q: How often should I reapply mineral sunscreen?
A: Reapply mineral sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
- Q: Are mineral sunscreens safe for sensitive skin?
A: Generally, yes. Mineral sunscreens are often preferred for sensitive skin as they are less likely to cause irritation or breakouts. However, it’s always recommended to test a small area of skin first to check for any reactions.
- Q: Do mineral sunscreens block all UV rays?
A: Mineral sunscreens offer broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays. However, they do not block 100% of UV radiation. It’s still important to practice other sun protection measures, such as wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses.
- Q: Can I use mineral sunscreen daily?
A: Yes, mineral sunscreens are safe for daily use. They can be incorporated into your regular skincare routine.
Tips for Using Non-Chemical Sunscreens:
-
Apply liberally and evenly: Use a generous amount of sunscreen and apply it evenly to all exposed skin.
-
Apply 20 minutes before sun exposure: Allow sunscreen to absorb into the skin before heading outdoors.
-
Reapply frequently: Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
-
Check the expiration date: Sunscreen loses its effectiveness over time. Replace expired sunscreen with a fresh bottle.
-
Store properly: Store sunscreen in a cool, dry place, out of direct sunlight.
Conclusion:
Non-chemical sunscreens provide a safe and effective way to protect your skin from the sun’s harmful rays. By choosing a mineral sunscreen, you can enjoy peace of mind knowing that you are using a product that is gentle on your skin, environmentally friendly, and provides comprehensive protection against the sun’s damaging effects. Remember to choose a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, apply it liberally and evenly, and reapply every two hours for optimal protection. By incorporating non-chemical sunscreen into your daily routine, you can protect your skin and maintain its health and vitality for years to come.
![]()






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Quest for Safe Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Non-Chemical Sunscreens. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!