The Quest for Accuracy: A Deep Dive into Language Selection for Google Translate
Related Articles: The Quest for Accuracy: A Deep Dive into Language Selection for Google Translate
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Quest for Accuracy: A Deep Dive into Language Selection for Google Translate. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Quest for Accuracy: A Deep Dive into Language Selection for Google Translate

Google Translate, a ubiquitous tool for bridging language barriers, relies on a complex interplay of algorithms and data to achieve its remarkable feat of translation. While the service boasts impressive capabilities, its success hinges on a crucial factor: the choice of language. The selection of the optimal language for translation significantly impacts the accuracy, fluency, and overall effectiveness of the output. This article delves into the intricacies of language selection for Google Translate, exploring the factors that influence its performance and the considerations for choosing the best language for specific translation needs.
Understanding the Nuances of Language:
Language is not merely a collection of words; it is a complex system interwoven with culture, history, and context. Each language possesses unique characteristics:
- Grammar and Syntax: The structure and organization of sentences vary widely across languages. For instance, English employs a subject-verb-object word order, while Japanese utilizes a subject-object-verb structure. These differences can pose challenges for translation algorithms.
- Vocabulary and Semantics: The meaning of words can be nuanced and context-dependent. A single word in one language may require several words or phrases to convey its full meaning in another.
- Idioms and Cultural References: Languages often incorporate idioms and cultural references that are specific to their respective cultures. These expressions can be difficult to translate accurately without losing their intended meaning.
The Role of Language Data in Google Translate:
Google Translate’s performance is heavily reliant on the quality and quantity of language data it has access to. This data includes:
- Parallel Corpora: Collections of texts in two or more languages that are aligned, allowing the system to learn correspondences between words and phrases.
- Monolingual Corpora: Large collections of text in a single language, providing insights into the language’s grammar, vocabulary, and usage patterns.
- User Feedback: Google Translate continuously learns from user feedback, which helps improve its translation accuracy and adapt to evolving language trends.
Factors Influencing Translation Accuracy:
The accuracy of Google Translate for a given language pair is influenced by several factors:
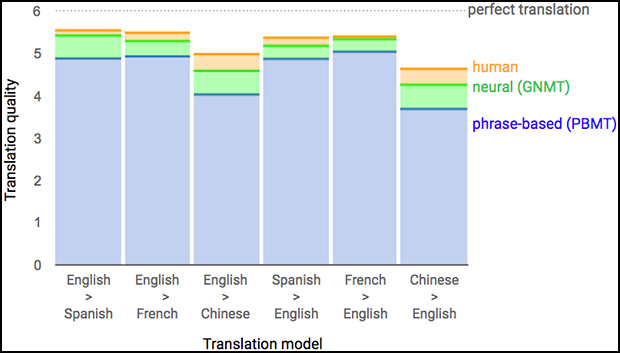
- Language Family: Languages belonging to the same family, such as Romance languages (French, Spanish, Italian) or Germanic languages (English, German, Dutch), tend to have more shared linguistic features, resulting in higher translation accuracy.
- Language Popularity: Languages with a larger corpus of available data, like English, Spanish, or French, generally achieve better translation accuracy.
- Translation Direction: The direction of translation (e.g., English to Spanish vs. Spanish to English) can impact accuracy. Languages with more data available in the target language often yield better results.
- Domain Specificity: Technical or specialized language, such as medical terminology or legal jargon, can pose challenges for Google Translate.
Choosing the Best Language for Google Translate:
Selecting the optimal language for Google Translate depends on the specific translation needs:
- High-Stakes Translations: For critical documents like legal contracts or medical reports, human translation is strongly recommended. Google Translate may be used as a supplementary tool to gain a general understanding but should not be relied upon for accuracy.
- Informal Communication: For casual communication, such as email exchanges or social media posts, Google Translate can be a valuable tool. However, it’s important to be mindful of potential inaccuracies and to double-check the translation for clarity.
- Language Learning: Google Translate can be a helpful tool for language learners, allowing them to understand basic phrases and vocabulary. However, it’s crucial to supplement its use with other learning resources to develop a comprehensive understanding of the language.
Tips for Maximizing Google Translate’s Accuracy:
- Choose the Correct Language Pair: Ensure that the source and target languages are accurately selected.
- Use Contextual Clues: Provide additional context to the text being translated, such as the topic, intended audience, and purpose of the translation.
- Review and Edit: Always review the translated text for accuracy and clarity. Make necessary edits to ensure that the meaning is conveyed correctly.
- Consider Using Other Translation Tools: For more formal or technical translations, consider using professional translation services or specialized translation software.
FAQs on Language Selection for Google Translate:
Q: What are the most accurate languages on Google Translate?
A: Languages with larger data sets and a closer linguistic relationship tend to achieve higher accuracy. English, Spanish, French, German, and Chinese are generally considered to be among the most accurate languages on Google Translate.
Q: Is Google Translate reliable for translating legal documents?
A: Google Translate is not recommended for translating legal documents. The nuances of legal language require expert translation to ensure accuracy and avoid misinterpretations.
Q: Can I use Google Translate for academic writing?
A: While Google Translate can provide a general understanding of academic texts, it’s not recommended for academic writing. Academic writing requires precise language and careful consideration of tone and style, which Google Translate may not fully capture.
Q: What should I do if Google Translate provides an inaccurate translation?
A: If you encounter an inaccurate translation, you can provide feedback directly to Google Translate. This feedback helps improve the system’s accuracy over time.
Conclusion:
The selection of the best language for Google Translate is a multifaceted decision influenced by the specific translation needs, the accuracy expectations, and the available resources. While Google Translate has made significant strides in its translation capabilities, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations and to use it judiciously. By understanding the factors influencing translation accuracy and following best practices, users can maximize the effectiveness of Google Translate as a valuable tool for bridging language barriers and fostering communication across cultures.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Quest for Accuracy: A Deep Dive into Language Selection for Google Translate. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!