The Evolution of Language Translation: A Deep Dive into Google’s Bard
Related Articles: The Evolution of Language Translation: A Deep Dive into Google’s Bard
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Evolution of Language Translation: A Deep Dive into Google’s Bard. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolution of Language Translation: A Deep Dive into Google’s Bard
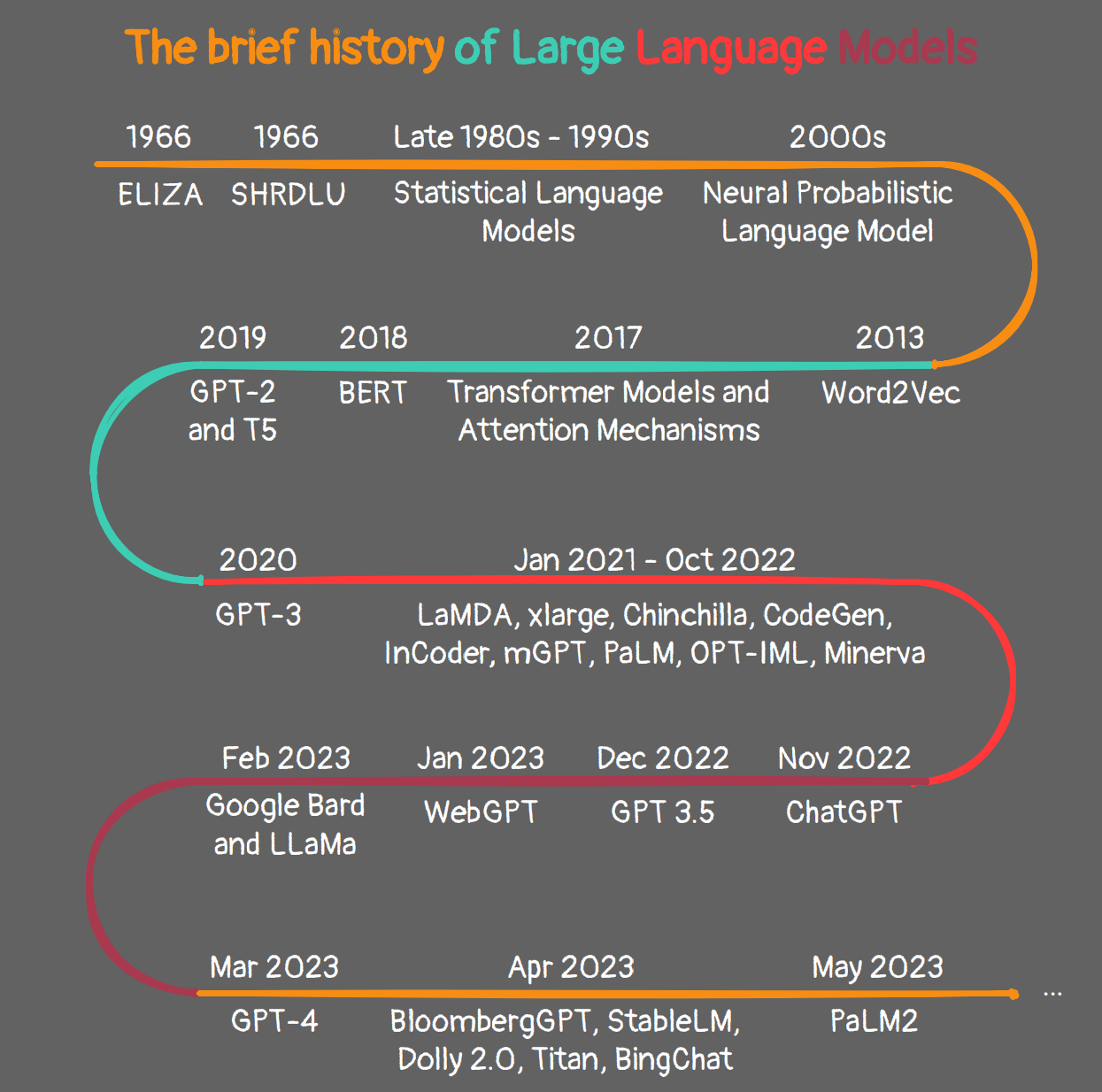
The realm of language translation has undergone a dramatic transformation, fueled by advancements in artificial intelligence. At the forefront of this revolution stands Google, with its innovative language model, Bard. While Bard is not directly integrated into Google Translate, it represents a significant leap forward in natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, paving the way for more nuanced and accurate translations in the future.
This article explores the intricate workings of Bard, its potential impact on language translation, and the broader implications for communication and cultural exchange.
Understanding the Core: Bard’s Capabilities and Architecture
Bard is a large language model (LLM) developed by Google AI. It is built upon the foundation of a transformer-based neural network, a powerful architecture that excels at processing sequential data like text. This architecture allows Bard to learn complex patterns and relationships within language, enabling it to generate human-like text, translate languages, write different kinds of creative content, and answer your questions in an informative way.
Beyond the Basics: Bard’s Distinctive Features
What sets Bard apart from traditional machine translation systems is its ability to:
- Understand context: Bard can analyze the surrounding text and understand the nuances of language, leading to more accurate and natural-sounding translations.
- Generate creative text: Bard can create different creative text formats, like poems, code, scripts, musical pieces, email, letters, etc. It can even help you answer your questions in a comprehensive and informative way.
- Adapt to different styles: Bard can adjust its translation style to suit the context, whether it’s formal, informal, or even humorous.
- Provide explanations: Bard can explain its reasoning behind a translation, offering users deeper insights into the process.
The Impact on Language Translation: A New Paradigm
Bard’s capabilities hold immense potential for revolutionizing language translation. Its advanced NLP abilities promise:
- More accurate translations: By understanding the nuances of language, Bard can produce translations that are closer to human-quality, minimizing errors and misinterpretations.
- Greater fluency and naturalness: Bard’s ability to generate human-like text ensures translations that flow smoothly and read naturally, enhancing comprehension and user experience.
- Improved cultural sensitivity: By recognizing cultural contexts and idioms, Bard can deliver translations that are culturally appropriate and avoid misinterpretations.
Beyond Translation: The Broader Implications of Bard
The impact of Bard extends beyond language translation, influencing a wide range of fields:
- Education: Bard can assist students with language learning, providing personalized feedback and explanations.
- Research: Bard can help researchers analyze large datasets of text, identify patterns, and generate insights.
- Customer service: Bard can power chatbots and virtual assistants, providing real-time support in multiple languages.
- Creative industries: Bard can assist writers, musicians, and artists by generating ideas, translating text, and even composing music.
FAQs about Bard
Q: What are the limitations of Bard?
A: While Bard has made significant strides, it still faces limitations. Its training data may not be entirely comprehensive, leading to potential biases or inaccuracies in certain contexts. Additionally, Bard may struggle with highly technical or specialized language, requiring further development.
Q: How does Bard differ from Google Translate?
A: Google Translate relies on statistical machine translation (SMT) and neural machine translation (NMT) techniques. While these methods have been successful, they often lack the nuance and context-awareness of Bard. Bard utilizes a more advanced LLM approach, enabling it to understand and generate more natural-sounding language.
Q: Is Bard publicly available?
A: Bard is currently in a limited testing phase, with access granted to a select group of users. Google plans to make Bard more widely available in the future.
Q: What are the ethical implications of Bard?
A: As with any powerful technology, there are ethical considerations surrounding Bard. It’s essential to ensure that Bard is used responsibly, avoiding potential biases and promoting fairness and transparency.
Tips for Utilizing Bard Effectively
- Provide clear and concise input: The quality of Bard’s output depends heavily on the quality of the input. Provide specific instructions and context for optimal results.
- Experiment with different prompts: Try various prompts and phrasing to explore Bard’s capabilities and find the best approach for your needs.
- Review and refine outputs: While Bard is highly capable, it’s always advisable to review its output and make any necessary adjustments for accuracy and clarity.
Conclusion: A Glimpse into the Future of Communication
Bard represents a significant leap forward in language translation, offering a glimpse into a future where communication barriers are minimized and cultural exchange is facilitated. As Bard continues to evolve and become more widely accessible, it has the potential to transform how we interact with language, learn, and create. The future of communication promises to be more seamless, dynamic, and inclusive, thanks to the transformative power of Bard and its ability to bridge the gap between languages and cultures.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolution of Language Translation: A Deep Dive into Google’s Bard. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
