Acne and Skin Care: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Breakouts
Related Articles: Acne and Skin Care: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Breakouts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Acne and Skin Care: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Breakouts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Acne and Skin Care: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Breakouts

Acne, a prevalent skin condition affecting millions worldwide, is characterized by the appearance of blemishes, pimples, and other inflammatory lesions on the skin. While often associated with adolescence, acne can manifest at any age, impacting both physical and psychological well-being. Understanding the intricacies of acne and its associated skin care practices is crucial for achieving clearer skin and enhancing overall confidence.
The Science Behind Acne
Acne arises from a complex interplay of factors, including genetics, hormones, bacteria, and inflammation. The process begins with the overproduction of sebum, an oily substance naturally produced by the skin’s sebaceous glands. This excess sebum, along with dead skin cells, can clog hair follicles, creating a conducive environment for the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) to proliferate.
P. acnes, a common inhabitant of the skin, thrives in these clogged follicles, triggering an inflammatory response. This inflammation manifests as red, swollen, and sometimes pus-filled lesions, commonly referred to as pimples or acne.
Types of Acne
Acne presents itself in various forms, each with its distinct characteristics:
- Whiteheads: Closed comedones, small white bumps that appear when a plugged follicle remains closed.
- Blackheads: Open comedones, characterized by a dark, oxidized plug within an open follicle.
- Papules: Small, raised, red, and inflamed lesions.
- Pustules: Similar to papules, but with a white or yellow center filled with pus.
- Nodules: Large, deep, and painful lesions that extend into the deeper layers of the skin.
- Cysts: Large, inflamed, and pus-filled lesions that can leave scarring.
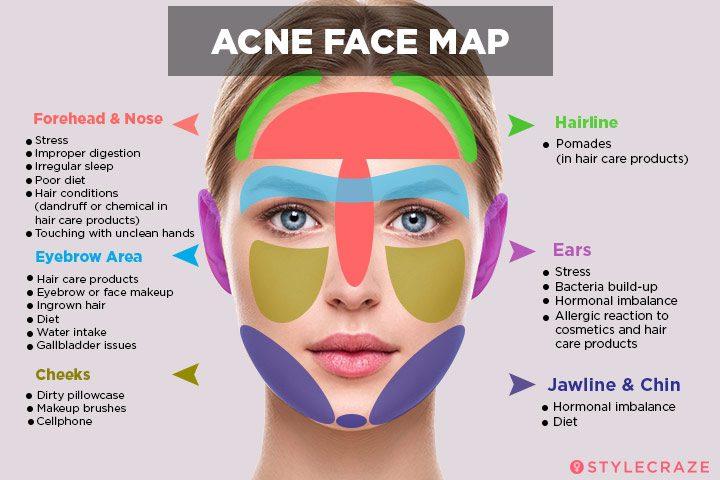
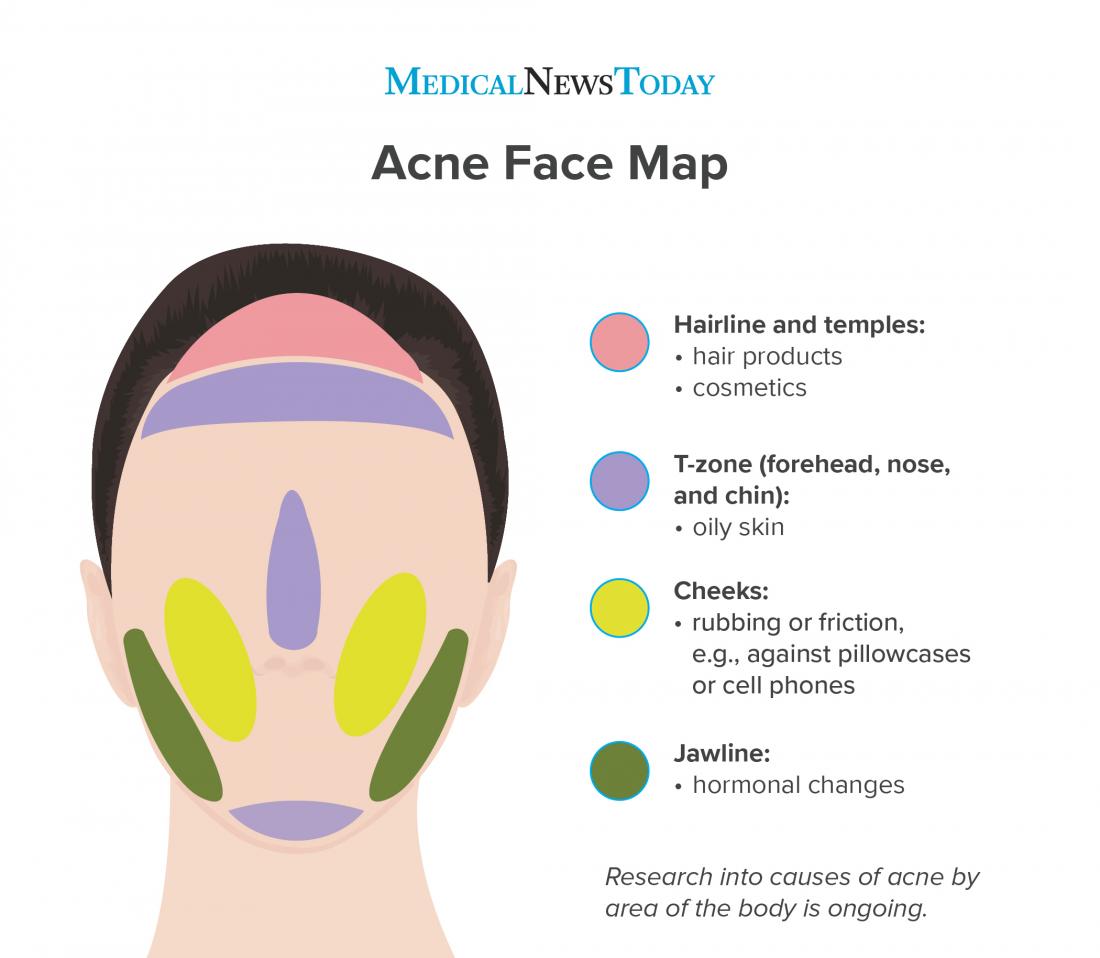
Factors Contributing to Acne
Several factors can contribute to the development of acne, including:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy, can trigger increased sebum production.
- Genetics: A family history of acne can increase an individual’s susceptibility to the condition.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids and lithium, can induce acne.
- Stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate acne by increasing hormone levels and inflammation.
- Diet: While the exact role of diet in acne remains under investigation, certain foods, such as dairy and refined carbohydrates, may contribute to breakouts.
- Cosmetics and skin care products: Certain ingredients, such as oil-based products and comedogenic (pore-clogging) substances, can worsen acne.
Skin Care Practices for Acne Management
Managing acne effectively requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses lifestyle modifications, over-the-counter (OTC) treatments, and, in some cases, prescription medications.
1. Cleansing:
- Gentle cleansing: Use a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser twice daily to remove dirt, oil, and makeup without irritating the skin. Avoid harsh soaps or scrubs that can strip the skin’s natural oils.
- Water temperature: Wash your face with lukewarm water, as hot water can dry out the skin and exacerbate inflammation.
2. Exfoliation:
- Regular exfoliation: Gently exfoliate the skin 1-2 times per week to remove dead skin cells and prevent clogged pores. Choose a gentle exfoliating scrub or chemical exfoliant containing ingredients like salicylic acid or glycolic acid.
- Avoid harsh scrubs: Avoid abrasive scrubs that can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
3. Moisturizing:
- Hydration is key: Even oily skin needs hydration. Choose a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer that does not clog pores.
- Moisturize twice daily: Apply moisturizer after cleansing to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
4. Sun Protection:
- Protect your skin: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Sunscreen helps prevent sun damage and hyperpigmentation, which can worsen acne scars.
5. Topical Treatments:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments: Several OTC medications are available for acne treatment, including benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and sulfur. These ingredients work by reducing bacteria, unclogging pores, and reducing inflammation.
- Prescription medications: For more severe acne, a dermatologist may prescribe topical medications such as retinoids (vitamin A derivatives), antibiotics, and combination therapies.
6. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Diet: While the role of diet in acne is complex, maintaining a healthy diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall skin health.
- Stress management: Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or yoga.
- Sleep hygiene: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to allow the body to repair and regenerate.
7. Professional Treatments:
- Dermatologist consultation: Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options.
- Chemical peels: Chemical peels can help remove dead skin cells and improve the appearance of acne scars.
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy can reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and stimulate collagen production.
- Microdermabrasion: Microdermabrasion uses a gentle abrasive device to remove dead skin cells and improve skin texture.
FAQs About Acne and Skin Care
1. What causes acne?
Acne arises from a combination of factors, including genetics, hormonal fluctuations, excess sebum production, clogged pores, and the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes.
2. Is acne contagious?
No, acne is not contagious. It is not caused by a virus or bacteria that can spread from person to person.
3. Does diet affect acne?
While the exact role of diet in acne is still under investigation, some studies suggest that certain foods, such as dairy and refined carbohydrates, may contribute to breakouts.
4. Can I pop pimples?
Popping pimples can worsen inflammation, increase the risk of scarring, and introduce bacteria into the skin, leading to further breakouts.
5. How long does it take to see results from acne treatment?
It can take several weeks or even months to see significant improvement in acne. Consistency with treatment is key.
6. Can acne be cured?
While acne cannot be permanently cured, it can be effectively managed and controlled with proper skin care practices and treatment.
7. Can I use makeup if I have acne?
Yes, you can use makeup if you have acne. However, choose non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging) products and avoid heavy makeup that can clog pores.
8. What can I do about acne scars?
Acne scars can be treated with various procedures, including chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion.
Tips for Acne and Skin Care
- Wash your hands before touching your face: This helps prevent the spread of bacteria that can contribute to acne.
- Keep your hair clean: Oil and dirt from your hair can transfer to your face and clog pores.
- Change your pillowcase regularly: Pillowcases can accumulate dirt, oil, and bacteria, which can contribute to acne.
- Avoid picking or squeezing pimples: This can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of scarring.
- Be patient: It takes time to see results from acne treatment. Don’t give up if you don’t see immediate improvement.
- Consult a dermatologist: If your acne is severe or persistent, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options.
Conclusion
Acne is a common skin condition that can have a significant impact on self-esteem and well-being. Understanding the underlying causes of acne and incorporating effective skin care practices can help manage breakouts and achieve clearer skin. A combination of lifestyle modifications, OTC treatments, and, in some cases, prescription medications can effectively control acne. Remember, consistency and patience are key to achieving long-term results. If you are struggling with acne, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options.


![]()
![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Acne and Skin Care: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Breakouts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!